QED.pl » Case studies » The project’s assumption is to use a bird’s eye view for a more effective down-to-earth business.
The task in this project was to use satellite images to recognize the situation on the ground. The project focuses on agricultural areas: identifying crops and their threats (anomalies) and segmenting satellite images based on the specific nature of the above.
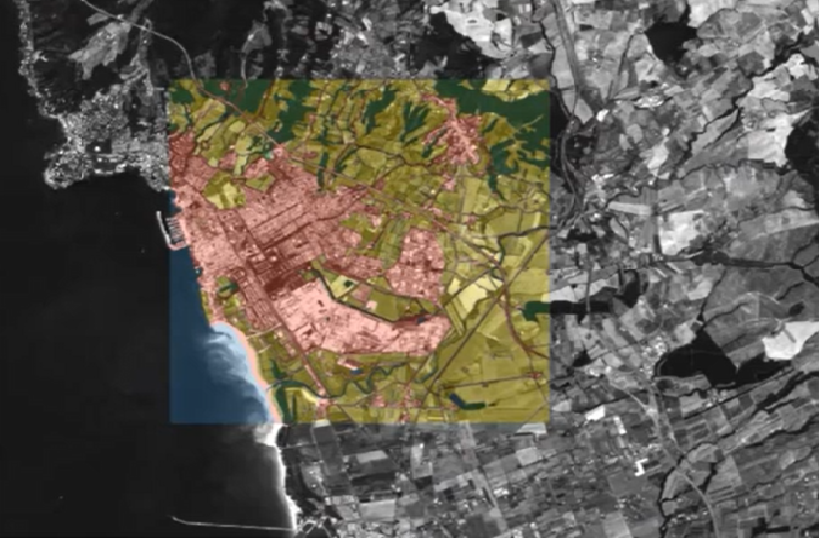


The company needed to develop and validate crop classification and change detection technology for crops, including detection of selected diseases and pests, based on satellite imagery.
The basis of the presented solution is using a deep neural network, which performs the image segmentation task.
The segmentation task itself is carried out gradually, by training successive neural networks. The first stage was the recognition of five basic land cover classes: low vegetation, high vegetation, urbanised (no-vegetation), water bodies, obscured (clouds, snow etc.). It is worth noting that in addition to the quantitative assessment, a qualitative visual assessment is also performed, which is particularly important in spatial data tasks. The next stage is the increasingly detailed identification of crops and anomalies in them.
The entire process was carried out in close cooperation with the client, who provides not only the input data for the learning process, but also the insight knowledge specific to his or her domain
Close cooperation is facilitated by using an innovative data labelling method called Label in the Loop (LitL). It supports the customer in the data labelling process, pointing out the parts of the data whose proper labelling is most important for the quality of the artificial neural network. Furthermore, the process is iterative, and the use of LitL technology reduces the amount of data needed for labelling, increasing the accuracy of the network results.

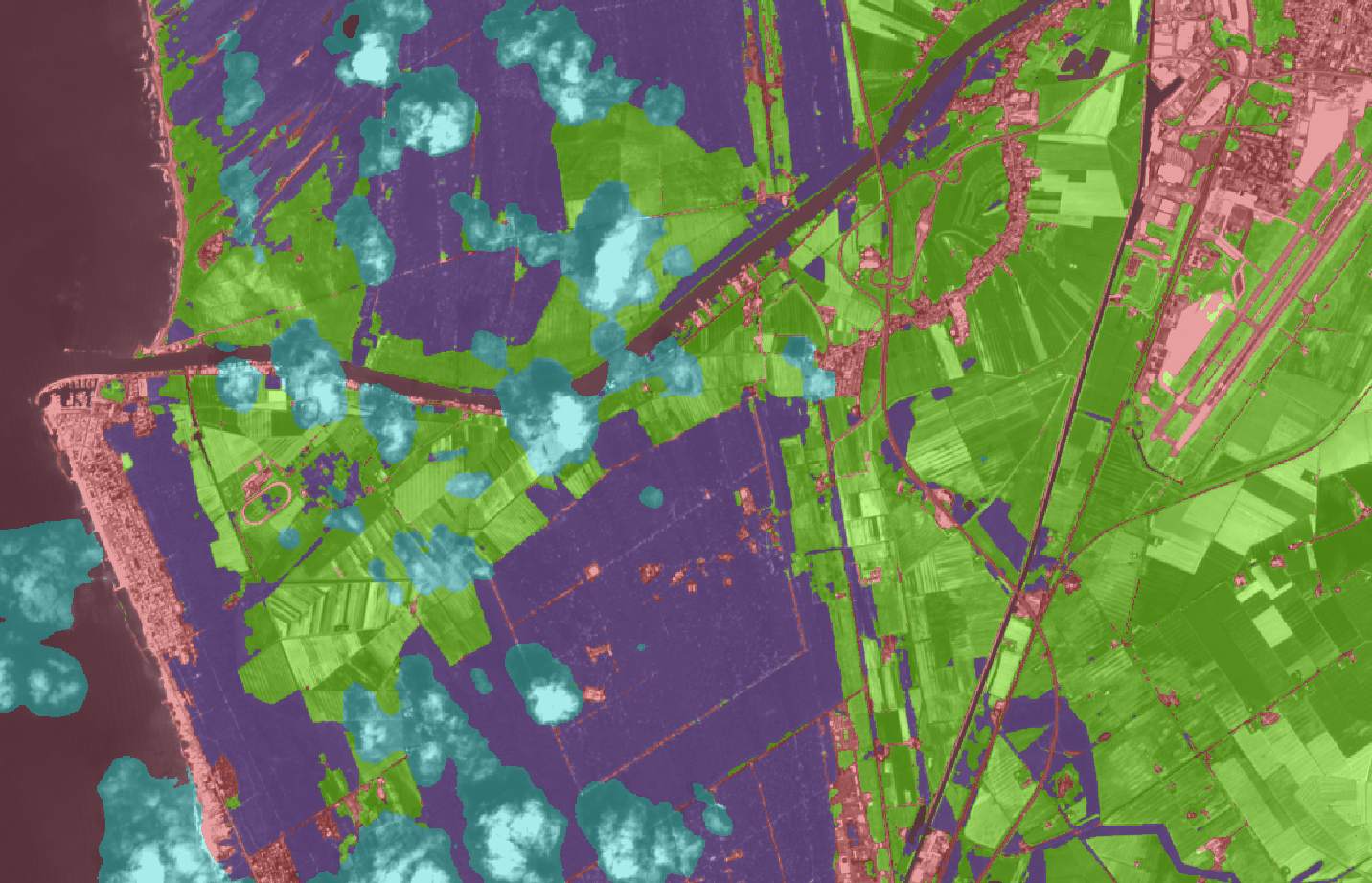
The Agrotech project is an example of advanced interdisciplinary cooperation between QED Software (AI, ML, NN), the customer (remote sensing), and domain specialists (agriculture).
The success of this project is directly related to the ability to recognize and understand the customer’s specialized needs and adjust the technology to the specificity of the industry in which the customer operates.
The process was iterative and the use of LitL technology reduced the amount of data required for tagging, increasing the accuracy of the web results.
As a result of the collaboration with the client/partner, a plug-in was created that implements the implemented functionality and can be further developed.
The product adapted to the environment (QGIS) and domain standards commonly used by both our client and its customers.
The project uses Label in the Loop (LitL) technology for an innovative way of tagging data.
AI for PIONEERS
Grow your business with artificial intelligence